Collagen is all the rage at the moment. Sure, it’s the holy grail for plump, youthful skin and a healthy body, but why is the world so obsessed with getting more of it? Is it best to down collagen powders, pills, and other tinctures to stay young? Or, are more tried-and-true methods the way to go? We investigate.
Meet the Experts
Dr. Rachel Maiman, is a board-certified general and cosmetic dermatologist.
Lisa Moskovitz, RD, CDN, CEO of New York Nutrition Group.
Dr. Benjamin Schuff, BIÂN Director of Naturopathy and Nutrition.
Terrie Absher Kochman, licensed clinical aesthetician and founder of Total Glow.
Dr. Chad Walding, DPT and co-founder of NativePath.
Collagen 101
Collagen is one of those buzzwords that’s everywhere right now. But there’s a reason why there is so much emphasis on this structural protein.
Naturally found in the skin’s dermis and connective tissue throughout the body, collagen provides support and structure so that the skin can sustain its plump, cushiony, and elastic appearance. Yes, it plays a substantial role in skin health, but collagen is responsible for more than just healthy skin — it’s necessary for strong joints, bones, muscles, ligaments, cartilage, and connective tissue. Simply put, it is a scaffolding protein that provides structure to whatever tissue it is contained in, says Dr. Rachel Maiman, a board-certified dermatologist.
Yet, with age and chronic exposure to the sun, smoke, pollution, stress, inflammatory diets and inflammation, and free radical damage, the amount and quality of said collagen starts to dip. By our 20s, the average person begins losing one percent of their collagen each year. And you know what that means, right? Yep, you guessed it — lines, wrinkles, and thin, sagging skin.
Unfortunately, there’s no way to evade the breakdown of collagen entirely, although it can be limited. The potential saving grace? It’s all about implementing a routine consisting of collagen-preserving and -stimulating products, treatments, and protocols sooner rather than later.

What collagen loos looks like
Most people don’t notice the effects of collagen loss (especially on the skin) when it’s first happening. Yet, it becomes more apparent once the impact — wrinkles, fine lines, a loss of elasticity, sagging, and more fragile skin — is accompanied by elastin degradation. “Other telling signs of collagen loss include joint pain and muscle weakness,” says Lisa Moskovitz, RD, CDN, CEO of NY Nutrition Group and author of The Core 3 Healthy Eating Plan.
There are about 16 known types of collagen within the body, and each has a slightly different chemical structure and function. “Unfortunately, the body’s ability to create new collagen structures loses efficiency,” says Dr. Ben Schuff, BIÂN Director of Naturopathy and Nutrition, adding that the rate of enzymatic breakdown of collagen (collagenase) increases as we age. “Think of collagen “loss” as more as a shift to less efficient collagen production, organization, retainment, and utilization,” he says.
Imagine the skin as a grape — it’s smooth, soft, and plump with no discernable signs of aging, like lines, wrinkles, and volume loss. Now, imagine the skin like a raisin — it’s tight and shriveled, lacks moisture and plumpness, and it’s covered in deep wrinkles, folds, and grooves. “Skin abundant in collagen (such as that in our 20s and earlier) is analogous to a grape — it’s plump and firm,” says Dr. Maiman. “As our collagen stores wane, we lose the dry weight of our dermis — collagen is the major constituent of the dermis, and collagens represent approximately 80% of the dry weight,” she adds. “This loss in volume results in loss of skin turgor and elasticity, which produces fine lines and wrinkles.”

Terrie Absher Kochman, licensed clinical aesthetician and founder of Total Glow, says that the desire for youthful-looking skin drives the continued search for ways to replace the collagen we naturally lose through aging or injury. “The foundation seems to fall out from under our skin; the plump suppleness starts to sag while lines and wrinkles become more apparent,” she adds.
As collagen levels deplete, it’s natural for the skin to start to thin out. “Collagen determines skin thickness, but as we lose it, our skin thins, which affects the underlying foundation,” says Kochman. The thicker the skin, the healthier it is because it is capable of supporting a strong foundation that’s elastic, able to hold moisture, soft, smooth, and more resistant to sagging and laxity.
The best collagen boosters
There is a ray of light at the end of the collagen loss tunnel. What’s lost can somewhat be replaced if you’re diligent about following a routine while avoiding collagen-damaging aggressors. From in-office treatments to ingestible powders and pills and serums and creams, there are tried-and-true methods to protect the existing collagen and stimulate healthy collagen production for more youthful skin and a stronger, healthier body. These are all the ways to do it.
Pills, Powders, and Beyond
The hot ticket of debate at the moment is collagen powders, pills, and supplements and if they work and are worth it.
Unlike the topical application of collagen-stimulating ingredients, collagen peptide-containing powders, supplements, and the such — there are even salmon skin collagen-promoting chips like Goodfish — employ one of two types of collagen: hydrolyzed collagen or gelatin.
Dr. Chad Walding, DPT and co-founder of NativePath, says that cooking down collagen creates gelatin, which breaks down the large protein into smaller collagen peptides that are more easily absorbed in the body. “Hydrolyzed collagen is essentially collagen hydrolysate,” he says. It’s important to recognize that all supplements are unregulated by the FDA, so while these products may be flooding your IG feed, knowing what you’re ingesting is key.
The primary purpose of a collagen supplement is to restore lost collagen. How much is restored is hard to pinpoint. Moskovitz says that ultimately, the body will break down the collagen and then disperse the amino acids to where they are needed most. So, it’s virtually impossible for collagen to be directed to a specific target area, like wrinkles around the mouth, for example. “However, that is not to say that it won’t help restore some collagen loss, but it is unlikely to produce a dramatic or noticeable difference.”
Clinical data on the actual benefits of ingestible collagen is somewhat lacking, too, so the community of skeptics seems to grow by the day. Dr. Maiman says that, to date, there’s little evidence that orally taking collagen does anything for the skin. “Some studies done in mice show evidence of more collagen peptides in the skin after ingestion, but the human digestive system is more robust than that of a rodent and breaks down collagen into simple amino acids before it can reach the dermis,” she explains. “Some brands have tried to circumvent this breakdown process by using hydrolyzed collagen, which is more readily absorbed by the gut, but it remains questionable how effective this is, and most data still suggests smaller collagen peptides are unable to induce clinically significant changes.” However, some data suggest it is beneficial in assisting with joint pain.
The Bottom Line: While there isn’t any harm in taking a collagen powder, pill, or supplement, don’t expect a quick or dramatic change in the quality of the skin — at this point, it’s pretty much anecdotal. However, Dr. Schuff adds that it does nothing to alter the natural genetic loss of internal collagen production or increased collagen enzymatic breakdown as we age. Therefore, one would require indefinite supplementation for minimal benefit.
Antioxidants
Antioxidants are an essential component of collagen conservation and production. That’s because antioxidants protect the delicate skin from free radicals and environmental damage. Moskowitz says that antioxidants, predominately found in plant-based foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and nuts, fight against stress and free radical damage that can chip away at collagen stores. Even antioxidant-rich green and matcha teas pack a powerful punch of collagen-stimulating powers — one of our favs is Pure Synergy Matcha Green Tea Powder, which can be enjoyed hot or blended into a smoothie.

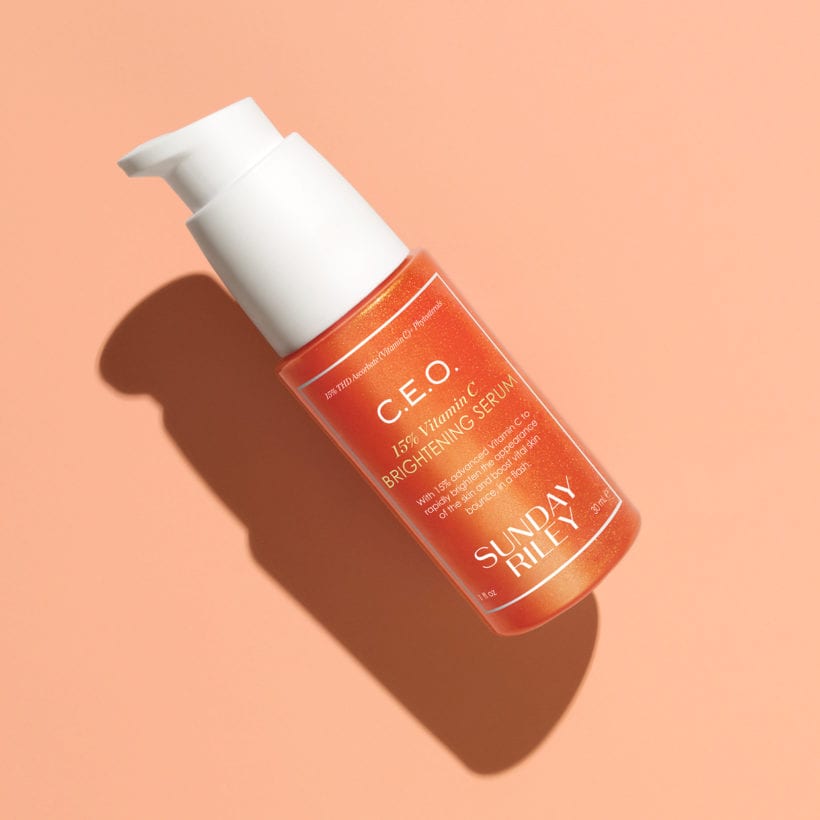
Consuming antioxidant-rich foods is as equally important as regularly using antioxidant-rich skincare products. “All antioxidants can fight free radical damage, but not all antioxidants boost collagen production, although they will help the collagen that is present to last,” Dr. Maiman shares. “Some antioxidants, though, like vitamin C, can stimulate the production of new collagen (vitamin C is an essential cofactor for the enzyme that makes collagen),” she says. Topically applying the vitamin to the skin in product forms, such as with Sunday Riley C.E.O. 15% Vitamin C Brightening Serum, will give a plumping and firming effect while reducing the signs of sun-related damage, like discoloration and spots.
One of the most effective methods of preserving collagen and preventing its degradation is the daily use of sunscreen. The sun is a known culprit of collagen breakdown that leads to wrinkles, fine lines, and age spots, so wear sunscreen every day, regardless of the weather or season. Look for skin-protecting formulas with at least SPF 30, found in Sunday Riley Light Hearted Broad Spectrum SPF 30 Sunscreen.
Retinols and Peptides
Collagen creams exist, although most experts and dermatologists feel they do little for the skin because of their considerably high molecular weight, preventing them from penetrating the skin appropriately. While these creams may feel good on the skin, lab-formulated collagen is too large for the skin to absorb adequately. Instead, the collagen sits on the skin’s surface, acting as a glorified moisturizing agent. Because collagen-containing creams do little, if anything, for the skin, retinol and peptides are more effective ingredients for creating new collagen.
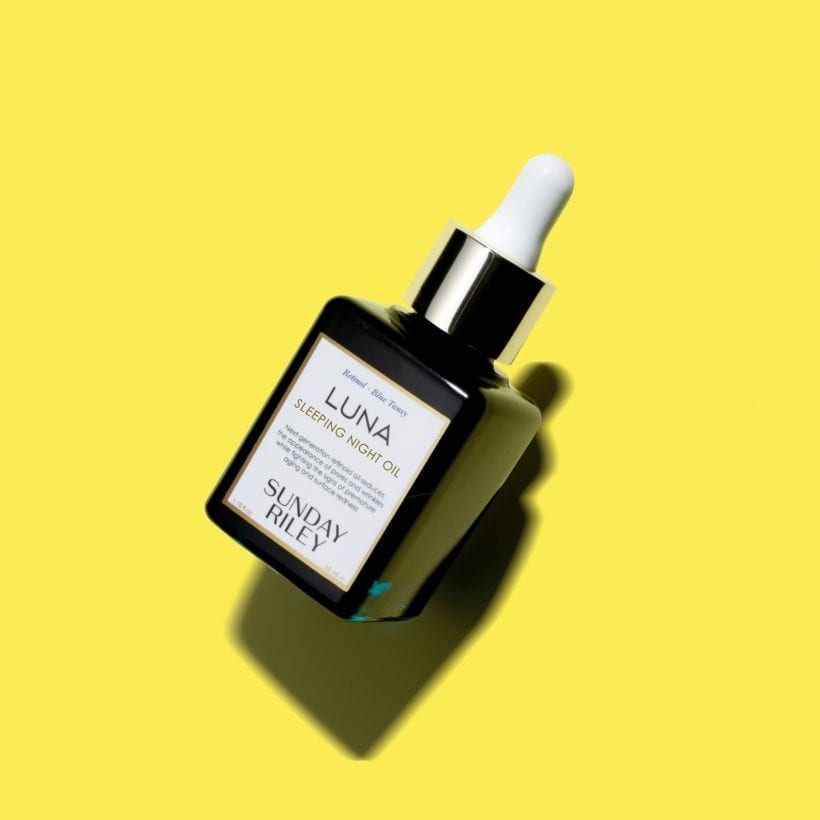
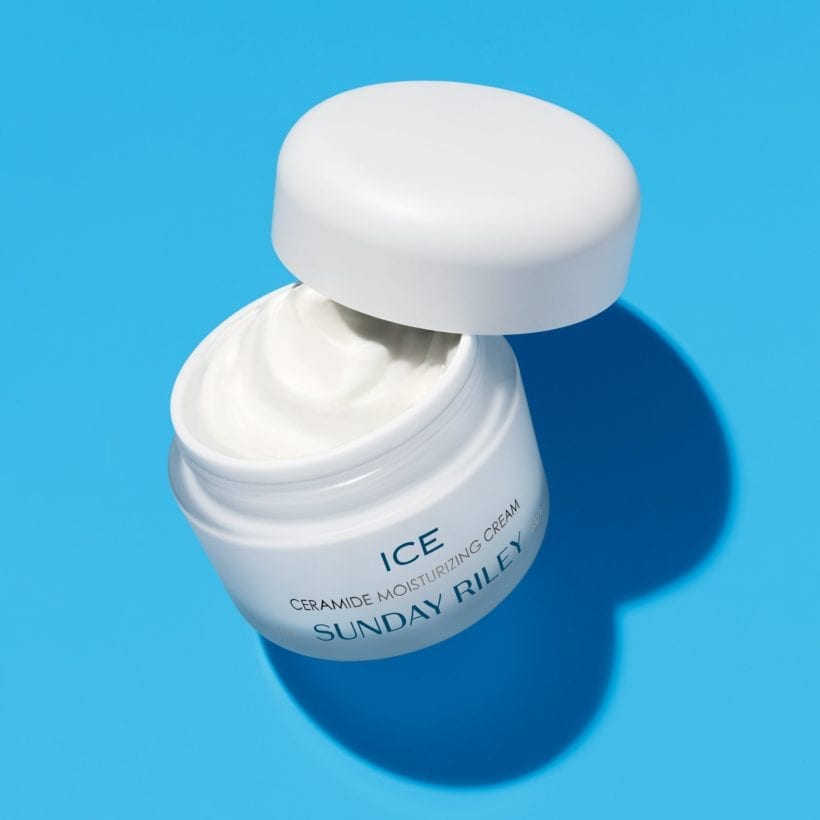
However, not all skin types are compatible with every concentration and formulation of retinol — it encourages faster skin cell turnover for increased collagen — so it is best to find a gentle yet effective formula that works for your skin type. If you are prone to dryness as a byproduct of using the vitamin A-derived ingredient, opt for retinol housed within an oil, like Sunday Riley Luna Sleeping Night Oil, which provides collagen-stimulating benefits in a hydrating base. Or, mix retinol, like Sunday Riley 5 Stars Retinoid + Niacinamide Eye Serum, with a ceramide-rich cream like Sunday Riley ICE Ceramide Moisturizing Cream.
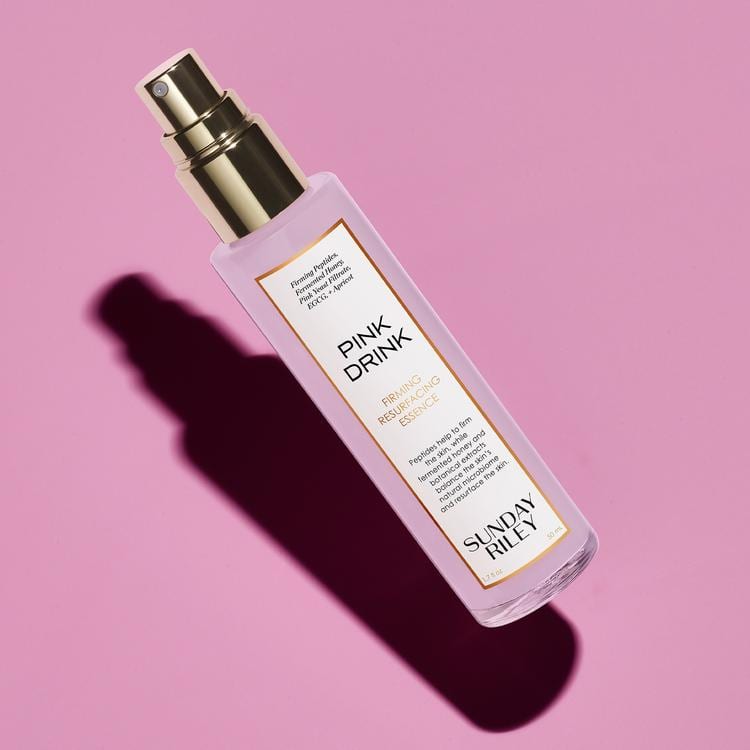
Peptides and the smaller-in-size collagen peptides work towards the same end goal as retinol in terms of collagen stimulation. They also help improve the quality of elastin in the skin (it’s responsible for making the skin more elastic with that bounce-back factor) to improve sagging and laxity. Applying a peptide-rich cream or -essence, like Sunday Riley Pink Drink Firming Resurfacing Essence, will help ‘turn on’ the skin’s ability to create new, healthy collagen. Plus, peptides work well with other collagen-stimulating ingredients like antioxidants, vitamin C, and moisturizing agents, so there’s no need to worry about interaction issues.
Other ingredients in skincare products help circumvent collagen loss, too, include niacinamide, ferulic acid, resveratrol, and certain botanical extracts, plus alpha hydroxy acids and growth factors.
Invest in in-office treatments
According to Dr. Maiman, most dermatologists agree that the best approach to stimulating collagen is utilizing effective topical ingredients in conjunction with in-office treatments. To make the most of your collagen-boosting efforts, invest in professional collagen-stimulating therapies or procedures that work at a deeper level than what at-home products can achieve (they’re still a much-needed part of the equation, so don’t write them off).
Consider resurfacing lasers, radiofrequency treatments, and microneedling, which are perhaps the most powerful collagen stimulators. “Resurfacing lasers can be fractionated, like Fraxel, Halo, Clear+Brilliant, and Profractional, or non-fractionated, like Contour TRL,” says Dr. Maiman. “These lasers induce thermal injury to the skin, and the process of wound healing involves the synthesis of new, better-organized collagen.”
Of-the-moment microneedling is an effective and accessible professional treatment for stimulating new collagen. It uses tiny needles to safely create micro-injuries in the skin, leading to new collagen creation (the treatment also improves pore size, discoloration, and acne scars). “Microneedling is similar in that it involves intentional tissue injury to stimulate collagen formation, though it is done through direct penetrative injury, rather than a thermal injury,” says Dr. Maiman. Plus, a wide variety of add-on treatments, like PRP and growth factors, are infused into the skin during or after the procedure to amp up the benefits further.
Radiofrequency and ultrasound treatments come in various strengths that use energy and heat to rev up collagen stimulation over several treatments. According to Dr. Maiman, radiofrequency can deliver heat to deeper levels of the skin, where it induces immediate tissue contraction and long-term collagen synthesis. “Although not routinely considered when one thinks of collagen-stimulating treatments, broadband light, like the Sciton BBL treatment, has also been shown to improve collagen density,” she adds.
When a loss of volume is a concern, biostimulatory fillers, like Radiesse and Sculptra Aesthetic, can provide long-term benefits when used under the skin as collagen forms around the product for added plumpness.
Finally, red-light therapies are also successful for increasing collagen production and plumping, tightening, and smoothing the skin for fewer lines. Unlike other options, they don’t require the use of a needle or laser nor any downtime, but their results are not as extreme. There are professional versions — some experts have full-body beds — and at-home versions, like Omnilux Contour Face and Current Body Skin LED Light Therapy Mask for easy access and maintenance.
We only recommend products we have independently researched, tested, and loved. If you purchase a product found through our links, Sunday Edit may earn an affiliate commission.













